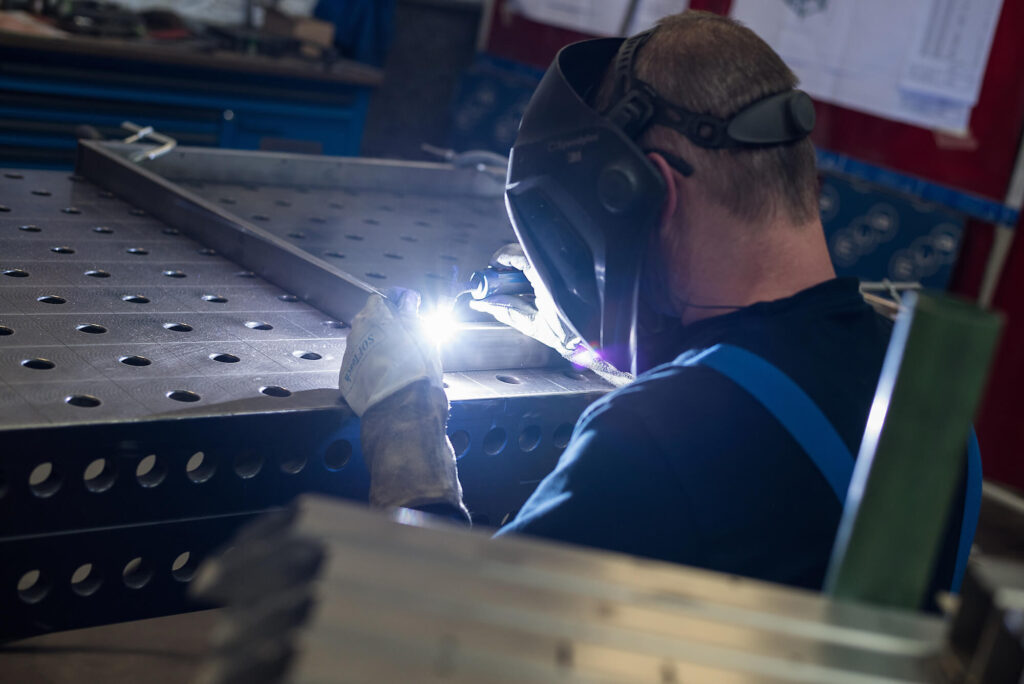
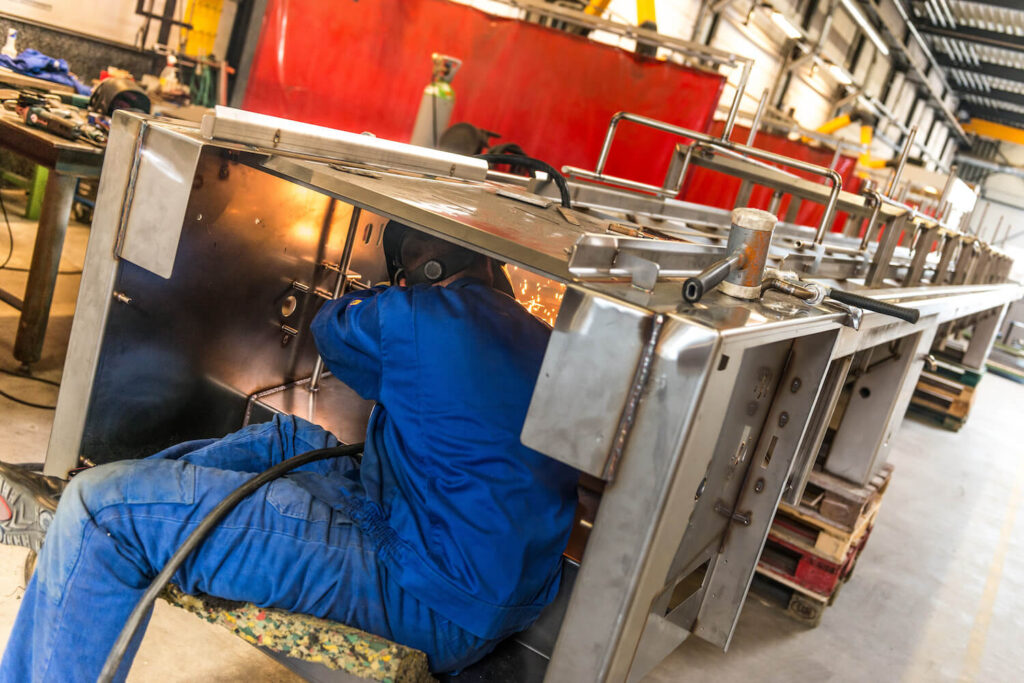
Top-class welding
Dumaco has more than one hundred manual welders; they are all specialists in their field. We also use robotic welding: for bigger product volumes and repeat products. This ensures that you are always able to rely on the very best quality. It also keeps turnaround times short.
We offer a number of types of welding technique. Basically, welding is a technique in which pressure and heat are used to bond materials together. Various filler metals can be used that have a big effect on the weld achieved and on the process too. At Dumaco, we weld both with and without filler metals.
We use the following manual welding techniques at Dumaco: TIG, MIG, MAG, stud and spot welding.
Why place your welding work with Dumaco?
Would you like to outsource every stage of your welding work? If so, Dumaco is the company for you. Preparations prior to welding and – of course – the welding work itself require a high level of precision. So, the use of qualified, experienced professionals, the right equipment and clamp tables are all essential. Dumaco is able to guarantee all of the above, at seven different sites.
TIG welding
TIG welding (Tungsten Inergt Gas) is a welding technique that we use regularly at Dumaco. We mainly use it when it’s important for a weld joint to be both precise and strong. The low welding speed makes it possible to work very precisely. TIG welding involves the formation of an arc between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The arc reaches a temperature of 14000°C, while the weld pool reaches a temperature of up to 7000°C. The shielding gas usually used is argon. TIG welding is an intensive and very precise welding technique. It’s ideal when wanting to achieve a high quality weld. We use a special TIG welding machine for TIG welding.
Applications for TIG welding
We use TIG welding for (stainless) steel and aluminum. TIG welding does not create any edges, so bacteria and dirt adhesion are not a problem. This is important for industries in which hygiene is essential (the food industry, for example). However, we regularly use TIG welding for various other industries as well. This is because TIG welding is very versatile. TIG welding creates very little spatter or welding fume. This means that the workpiece looks representative at all times. Finally, TIG welding is the best technique to use when welding thinner sheets of metal.
The advantages of TIG welding
- Good weld quality
- No coating, no slag
- Very little heat input
- High duty-cycle
- Good protection against oxidation
- Application in every position
MIG and MAG welding
MIG and MAG welding are often named in the same breath. However, there is a small difference between these welding techniques: the gas mixture used. MIG is the abbreviation for Metal Inert Gas, while MAG stands for Metal Active Gas. Gas is used to protect the weld pool. MIG and MAG welding are both constant-voltage welding technique. This means that a constant voltage is applied between the welding rod and the workpiece. The welding rod is both the electrode and the filler metal here. MIG and MAG welding are both popular techniques in the welding world and are used a lot at Dumaco as well.
Applications for MIG and MAG welding
We use these techniques to weld steel (MAG welding) and stainless steel and aluminum (MIG welding). MAG welding is mainly used for non-alloy and low-alloy steels. MIG welding is used to bond high-alloy and stainless steels. MIG and MAG welding make it possible to weld quickly and achieve a high-quality weld. MIG pulse welding is possible too. This technique creates less heat and makes it easier to weld thin material. We mainly use MIG pulse welding to weld aluminum.
The advantages of MIG and MAG welding
- Good weld quality
- High welding speed
- Very little heat input
- A relatively ‘cheap’ welding technique when using CO2 (MAG welding)
- Applicable in virtually every welding position
- Provides good oxidation protection
Stud welding
Stud welding (also called butt welding) involves the ignition of an arc between one end of the stud and the workpiece. Stud welding can be done both with a robot and manually. Manual stud welding services are offered at every Dumaco site. Where series work is concerned, we consider whether automated processing would be possible at one of our sites. Read more about stud welding.
Spot welding
Spot welding involves the application of pressure and heat to bond metal surfaces together. The tips on the machine – which is where the electrodes are located – are quite small. Because of this, the current generated is concentrated on a small area. We spot-weld (stainless) steel and aluminum. Weld nuts can be spotted welded too.
Certified welding
Dumaco employs certified welders at all its sites. Dumaco has a number of certifications, including ISO 3834-2 and EN 1090. We formulate WPSs, PRQs and WPQs on a daily basis. Weld, material and certified-welder traceability are possible too. Dumaco Oss, Dumaco Woerden and Dumaco Montfoort are able to provide certified welding. Contact us for more information.




 Standard quotations are always issued within 24 hours
Standard quotations are always issued within 24 hours







